German New Guinea
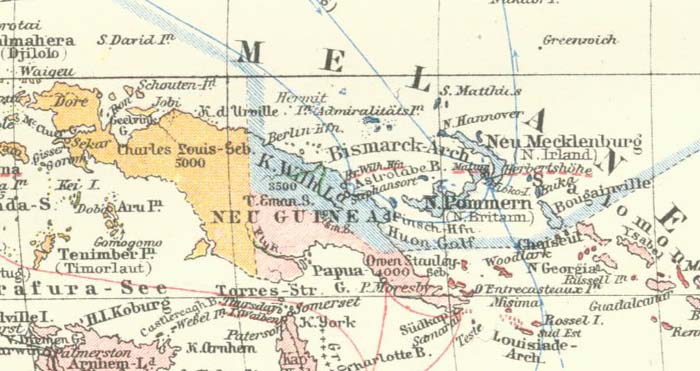
New Guinea, after Greenland the second largest island in the world is situated north of Australia, part of the Australian Plate. With an area of about 772,000 sq. kms (of which the German part covered some 179,000 ) the island is more than twice the size of present day Germany. A mountain range some 2000 kms in length extends from East to West, with glaciers and summits reaching 5000 m. Its geographical position is between 130 and 151 degrees longitude East and 1 and 11 degrees latitude South . The climate is typically tropical with heavy rainfall.
Adjoining groups of islands which were also part of the colony were equally mountainous with heights, some volcanic, rising to 2,400 m. The Bismarck Archipelago included the Admiralty Isles and some smaller groups in the North such as New Hanover, New Mecklenburg and New Pomerania. The northernmost islands of the Solomon Group, Buka and Bougainville also belonged to the colony. Originally Shortland Island, Choiseul and Santa Ysabel were also a part but were ceded to England by the Samoa Treaty of 1899.